RPC框架简介
RPC,即 Remote Procedure Call(远程过程调用),说得通俗一点就是:调用远程计算机上的服务,就像调用本地服务一样。
RPC 可基于 HTTP 或 TCP 协议,Web Service 就是基于 HTTP 协议的 RPC,它具有良好的跨平台性,但其性能却不如基于 TCP 协议的 RPC。会两方面会直接影响 RPC 的性能,一是传输方式,二是序列化。
众所周知,TCP 是传输层协议,HTTP 是应用层协议,而传输层较应用层更加底层,在数据传输方面,越底层越快,因此,在一般情况下,TCP 一定比 HTTP 快。就序列化而言,Java 提供了默认的序列化方式,但在高并发的情况下,这种方式将会带来一些性能上的瓶颈,于是市面上出现了一系列优秀的序列化框架,比如:Protobuf、Kryo、Hessian、Jackson 等,它们可以取代 Java 默认的序列化,从而提供更高效的性能。
为了支持高并发,传统的阻塞式 IO 显然不太合适,因此我们需要异步的 IO,即 NIO。Java 提供了 NIO 的解决方案,Java 7 也提供了更优秀的 NIO.2 支持,用 Java 实现 NIO 并不是遥不可及的事情,只是需要我们熟悉 NIO 的技术细节。
我们需要将服务部署在分布式环境下的不同节点上,通过服务注册的方式,让客户端来自动发现当前可用的服务,并调用这些服务。这需要一种服务注册表(Service Registry)的组件,让它来注册分布式环境下所有的服务地址(包括:主机名与端口号)。
应用、服务、服务注册表之间的关系见下图:
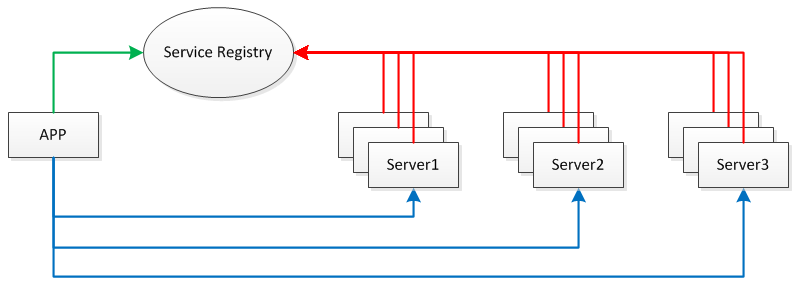
每台 Server 上可发布多个 Service,这些 Service 共用一个 host 与 port,在分布式环境下会提供 Server 共同对外提供 Service。此外,为防止 Service Registry 出现单点故障,因此需要将其搭建为集群环境。
本文将为您揭晓开发轻量级分布式 RPC 框架的具体过程,该框架基于 TCP 协议,提供了 NIO 特性,提供高效的序列化方式,同时也具备服务注册与发现的能力。
根据以上技术需求,我们可使用如下技术选型:
- Spring:它是最强大的依赖注入框架,也是业界的权威标准。
- Netty:它使 NIO 编程更加容易,屏蔽了 Java 底层的 NIO 细节。
- Protostuff:它基于 Protobuf 序列化框架,面向 POJO,无需编写 .proto 文件。
- ZooKeeper:提供服务注册与发现功能,开发分布式系统的必备选择,同时它也具备天生的集群能力。
项目结构
- rpc-client:RpcClient用于发送RPC请求,RpcProxy用于创建 RPC 服务代理
- rpc-common:RpcRequest封装 RPC 请求,RpcResponse封装 RPC 响应,RpcDecoderRPC 解码器,RpcEncoderRPC 编码器
- rpc-registry:ServiceDiscovery服务发现接口,ServiceRegistry服务注册接口
- rpc-registry-zookeeper:Constant常量,ZooKeeperServiceDiscovery基于 ZooKeeper 的服务发现接口实现,ZooKeeperServiceRegistry基于 ZooKeeper 的服务注册接口实现
- rpc-server:RpcServer-RPC 服务器(用于发布 RPC 服务),RpcServerHandler服务端处理器(用于处理 RPC 请求),RpcService服务注解(标注在服务实现类上)
- rpc-sample-api:示例服务接口HelloService,实体类Person
- rpc-sample-client:调用示例服务接口
- rpc-sample-server:RpcBootstrap启动RPC服务器,HelloServiceImpl服务接口实现类
服务端调用过程
准备阶段:安装Zookeeper,并创建/registry永久节点,用于存放所有的服务临时节点。
参见上篇博客:Zookeeper简介
启动服务器
为了加载 Spring 配置文件来发布服务,只需编写一个引导程序即可:
// rpc-sample-server
public class RpcBootstrap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LOGGER.debug("start server");
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
}
}
输出:
start server
connect zookeeper
create service node: /registry/com.xxx.rpc.sample.api.HelloService
create address node: /registry/com.xxx.rpc.sample.api.HelloService/address-0000000000
register service: com.xxx.rpc.sample.api.HelloService => 127.0.0.1:8000
create service node: /registry/com.xxx.rpc.sample.api.HelloService-sample.hello2
create address node: /registry/com.xxx.rpc.sample.api.HelloService-sample.hello2/address-0000000000
register service: com.xxx.rpc.sample.api.HelloService-sample.hello2 => 127.0.0.1:8000
server started on port 8000
Spring加载配置
spring.xml文件,生成serviceRegistry对象,构造参数是zookeeper地址;生成rpcServer对象,构造参数是服务器地址和注册对象
<context:component-scan base-package="com.xxx.rpc.sample.server"/>
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:rpc.properties"/>
<bean id="serviceRegistry" class="com.xxx.rpc.registry.zookeeper.ZooKeeperServiceRegistry">
<constructor-arg name="zkAddress" value="${rpc.registry_address}"/>
</bean>
<bean id="rpcServer" class="com.xxx.rpc.server.RpcServer">
<constructor-arg name="serviceAddress" value="${rpc.service_address}"/>
<constructor-arg name="serviceRegistry" ref="serviceRegistry"/>
</bean>
具体配置参数rpc.properties
rpc.service_address=127.0.0.1:8000
rpc.registry_address=127.0.0.1:2181
服务注册serviceRegistry
使用 ZooKeeper 客户端可轻松实现服务注册功能,ServiceRegistry代码如下
public class ZooKeeperServiceRegistry implements ServiceRegistry {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ZooKeeperServiceRegistry.class);
private final ZkClient zkClient;
public ZooKeeperServiceRegistry(String zkAddress) {
// 创建 ZooKeeper 客户端
zkClient = new ZkClient(zkAddress, Constant.ZK_SESSION_TIMEOUT, Constant.ZK_CONNECTION_TIMEOUT);
LOGGER.debug("connect zookeeper");
}
@Override
public void register(String serviceName, String serviceAddress) {
// 创建 registry 节点(持久)
String registryPath = Constant.ZK_REGISTRY_PATH;
if (!zkClient.exists(registryPath)) {
zkClient.createPersistent(registryPath);
LOGGER.debug("create registry node: {}", registryPath);
}
// 创建 service 节点(持久)
String servicePath = registryPath + "/" + serviceName;
if (!zkClient.exists(servicePath)) {
zkClient.createPersistent(servicePath);
LOGGER.debug("create service node: {}", servicePath);
}
// 创建 address 节点(临时)
String addressPath = servicePath + "/address-";
String addressNode = zkClient.createEphemeralSequential(addressPath, serviceAddress);
LOGGER.debug("create address node: {}", addressNode);
}
}
其中,通过Constant配置了所有的常量:
public interface Constant {
int ZK_SESSION_TIMEOUT = 5000;
int ZK_CONNECTION_TIMEOUT = 1000;
String ZK_REGISTRY_PATH = "/registry";
}
实现RPC服务器rpcServer
使用 Netty 可实现一个支持 NIO 的 RPC 服务器,需要使用ServiceRegistry注册服务地址,RpcServer代码如下:
public class RpcServer implements ApplicationContextAware, InitializingBean {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RpcServer.class);
private String serviceAddress;
private ServiceRegistry serviceRegistry;
/**
* 存放 服务名 与 服务对象 之间的映射关系
*/
private Map<String, Object> handlerMap = new HashMap<>();
public RpcServer(String serviceAddress) {
this.serviceAddress = serviceAddress;
}
public RpcServer(String serviceAddress, ServiceRegistry serviceRegistry) {
this.serviceAddress = serviceAddress;
this.serviceRegistry = serviceRegistry;
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext ctx) throws BeansException {
// 扫描带有 RpcService 注解的类并初始化 handlerMap 对象
Map<String, Object> serviceBeanMap = ctx.getBeansWithAnnotation(RpcService.class);
if (MapUtils.isNotEmpty(serviceBeanMap)) {
for (Object serviceBean : serviceBeanMap.values()) {
RpcService rpcService = serviceBean.getClass().getAnnotation(RpcService.class);
String serviceName = rpcService.value().getName();
String serviceVersion = rpcService.version();
if (StringUtil.isNotEmpty(serviceVersion)) {
serviceName += "-" + serviceVersion;
}
handlerMap.put(serviceName, serviceBean);
}
}
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
// 创建并初始化 Netty 服务端 Bootstrap 对象
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup);
bootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel channel) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = channel.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(new RpcDecoder(RpcRequest.class)); // 解码 RPC 请求
pipeline.addLast(new RpcEncoder(RpcResponse.class)); // 编码 RPC 响应
pipeline.addLast(new RpcServerHandler(handlerMap)); // 处理 RPC 请求
}
});
bootstrap.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024);
bootstrap.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true);
// 获取 RPC 服务器的 IP 地址与端口号
String[] addressArray = StringUtil.split(serviceAddress, ":");
String ip = addressArray[0];
int port = Integer.parseInt(addressArray[1]);
// 启动 RPC 服务器
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind(ip, port).sync();
// 注册 RPC 服务地址
if (serviceRegistry != null) {
for (String interfaceName : handlerMap.keySet()) {
serviceRegistry.register(interfaceName, serviceAddress);
LOGGER.debug("register service: {} => {}", interfaceName, serviceAddress);
}
}
LOGGER.debug("server started on port {}", port);
// 关闭 RPC 服务器
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
RpcService 注解扫描
该注解具备 Spring 的Component注解的特性,可被 Spring 扫描。
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Component
public @interface RpcService {
/**
* 服务接口类
*/
Class<?> value();
/**
* 服务版本号
*/
String version() default "";
}
使用RpcService注解定义在服务接口的实现类上,需要对该实现类指定远程接口,因为实现类可能会实现多个接口,一定要告诉框架哪个才是远程接口。
@RpcService(HelloService.class)
public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {
@Override
public String hello(String name) {
return "Hello! " + name;
}
@Override
public String hello(Person person) {
return "Hello! " + person.getFirstName() + " " + person.getLastName();
}
}
服务端处理器RpcServerHandler
使用RpcHandler中处理 RPC 请求,只需扩展 Netty 的SimpleChannelInboundHandler抽象类即可,代码如下。为了避免使用 Java 反射带来的性能问题,我们可以使用 CGLib 提供的反射 API,如下面用到的FastClass与FastMethod。
public class RpcServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<RpcRequest> {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RpcServerHandler.class);
private final Map<String, Object> handlerMap;
public RpcServerHandler(Map<String, Object> handlerMap) {
this.handlerMap = handlerMap;
}
@Override
public void channelRead0(final ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcRequest request) throws Exception {
// 创建并初始化 RPC 响应对象
RpcResponse response = new RpcResponse();
response.setRequestId(request.getRequestId());
try {
Object result = handle(request);
response.setResult(result);
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error("handle result failure", e);
response.setException(e);
}
// 写入 RPC 响应对象并自动关闭连接
ctx.writeAndFlush(response).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);
}
private Object handle(RpcRequest request) throws Exception {
// 获取服务对象
String serviceName = request.getInterfaceName();
String serviceVersion = request.getServiceVersion();
if (StringUtil.isNotEmpty(serviceVersion)) {
serviceName += "-" + serviceVersion;
}
Object serviceBean = handlerMap.get(serviceName);
if (serviceBean == null) {
throw new RuntimeException(String.format("can not find service bean by key: %s", serviceName));
}
// 获取反射调用所需的参数
Class<?> serviceClass = serviceBean.getClass();
String methodName = request.getMethodName();
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = request.getParameterTypes();
Object[] parameters = request.getParameters();
// 执行反射调用
// Method method = serviceClass.getMethod(methodName, parameterTypes);
// method.setAccessible(true);
// return method.invoke(serviceBean, parameters);
// 使用 CGLib 执行反射调用
FastClass serviceFastClass = FastClass.create(serviceClass);
FastMethod serviceFastMethod = serviceFastClass.getMethod(methodName, parameterTypes);
return serviceFastMethod.invoke(serviceBean, parameters);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
LOGGER.error("server caught exception", cause);
ctx.close();
}
}
使用RpcRequest封装 RPC 请求,代码如下:
public class RpcRequest {
private String requestId;
private String className;
private String methodName;
private Class<?>[] parameterTypes;
private Object[] parameters;
// getter/setter...
}
使用RpcResponse封装 RPC 响应,代码如下:
public class RpcResponse {
private String requestId;
private Throwable error;
private Object result;
// getter/setter...
}
使用RpcDecoder提供 RPC 解码,只需扩展 Netty 的ByteToMessageDecoder抽象类的decode方法即可,代码如下:
public class RpcDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder {
private Class<?> genericClass;
public RpcDecoder(Class<?> genericClass) {
this.genericClass = genericClass;
}
@Override
public void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
if (in.readableBytes() < 4) {
return;
}
in.markReaderIndex();
int dataLength = in.readInt();
if (in.readableBytes() < dataLength) {
in.resetReaderIndex();
return;
}
byte[] data = new byte[dataLength];
in.readBytes(data);
out.add(SerializationUtil.deserialize(data, genericClass));
}
}
使用RpcEncoder提供 RPC 编码,只需扩展 Netty 的MessageToByteEncoder抽象类的encode方法即可,代码如下:
public class RpcEncoder extends MessageToByteEncoder {
private Class<?> genericClass;
public RpcEncoder(Class<?> genericClass) {
this.genericClass = genericClass;
}
@Override
public void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object in, ByteBuf out) throws Exception {
if (genericClass.isInstance(in)) {
byte[] data = SerializationUtil.serialize(in);
out.writeInt(data.length);
out.writeBytes(data);
}
}
}
编写一个SerializationUtil工具类,使用Protostuff实现序列化:
public class SerializationUtil {
private static Map<Class<?>, Schema<?>> cachedSchema = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private static Objenesis objenesis = new ObjenesisStd(true);
private SerializationUtil() {
}
/**
* 序列化(对象 -> 字节数组)
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static <T> byte[] serialize(T obj) {
Class<T> cls = (Class<T>) obj.getClass();
LinkedBuffer buffer = LinkedBuffer.allocate(LinkedBuffer.DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE);
try {
Schema<T> schema = getSchema(cls);
return ProtostuffIOUtil.toByteArray(obj, schema, buffer);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(), e);
} finally {
buffer.clear();
}
}
/**
* 反序列化(字节数组 -> 对象)
*/
public static <T> T deserialize(byte[] data, Class<T> cls) {
try {
T message = objenesis.newInstance(cls);
Schema<T> schema = getSchema(cls);
ProtostuffIOUtil.mergeFrom(data, message, schema);
return message;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private static <T> Schema<T> getSchema(Class<T> cls) {
Schema<T> schema = (Schema<T>) cachedSchema.get(cls);
if (schema == null) {
schema = RuntimeSchema.createFrom(cls);
cachedSchema.put(cls, schema);
}
return schema;
}
}
以上了使用 Objenesis 来实例化对象,它是比 Java 反射更加强大。
注意:如需要替换其它序列化框架,只需修改SerializationUtil即可。当然,更好的实现方式是提供配置项来决定使用哪种序列化方式。
客户端调用过程
启动客户端
rpc-sample-client创建服务对象并调用,同样使用 Spring 配置文件来配置 RPC 客户端:
public class HelloClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
RpcProxy rpcProxy = context.getBean(RpcProxy.class);
HelloService helloService = rpcProxy.create(HelloService.class);
String result = helloService.hello("World");
System.out.println(result);
HelloService helloService2 = rpcProxy.create(HelloService.class, "sample.hello2");
String result2 = helloService2.hello("世界");
System.out.println(result2);
System.exit(0);
}
}
打印结果:
connect zookeeper
get only address node: address-0000000001
discover service: com.xxx.rpc.sample.api.HelloService => 127.0.0.1:8000
time: 789ms
Hello! World
connect zookeeper
get only address node: address-0000000001
discover service: com.xxx.rpc.sample.api.HelloService-sample.hello2 => 127.0.0.1:8000
time: 11ms
你好! 世界
Spring加载配置
spring.xml生成了对象serviceDiscovery,构造参数是Zookeeper地址;生成了对象RpcProxy,构造参数是serviceDiscovery
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:rpc.properties"/>
<bean id="serviceDiscovery" class="com.xxx.rpc.registry.zookeeper.ZooKeeperServiceDiscovery">
<constructor-arg name="zkAddress" value="${rpc.registry_address}"/>
</bean>
<bean id="rpcProxy" class="com.xxx.rpc.client.RpcProxy">
<constructor-arg name="serviceDiscovery" ref="serviceDiscovery"/>
</bean>
rpc-properties配置
rpc.registry_address=127.0.0.1:2181
实现服务发现serviceDiscovery
同样使用 ZooKeeper 实现服务发现功能,见如下代码:
public class ZooKeeperServiceDiscovery implements ServiceDiscovery {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ZooKeeperServiceDiscovery.class);
private String zkAddress;
public ZooKeeperServiceDiscovery(String zkAddress) {
this.zkAddress = zkAddress;
}
@Override
public String discover(String name) {
// 创建 ZooKeeper 客户端
ZkClient zkClient = new ZkClient(zkAddress, Constant.ZK_SESSION_TIMEOUT, Constant.ZK_CONNECTION_TIMEOUT);
LOGGER.debug("connect zookeeper");
try {
// 获取 service 节点
String servicePath = Constant.ZK_REGISTRY_PATH + "/" + name;
if (!zkClient.exists(servicePath)) {
throw new RuntimeException(String.format("can not find any service node on path: %s", servicePath));
}
List<String> addressList = zkClient.getChildren(servicePath);
if (CollectionUtil.isEmpty(addressList)) {
throw new RuntimeException(String.format("can not find any address node on path: %s", servicePath));
}
// 获取 address 节点
String address;
int size = addressList.size();
if (size == 1) {
// 若只有一个地址,则获取该地址
address = addressList.get(0);
LOGGER.debug("get only address node: {}", address);
} else {
// 若存在多个地址,则随机获取一个地址
address = addressList.get(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(size));
LOGGER.debug("get random address node: {}", address);
}
// 获取 address 节点的值
String addressPath = servicePath + "/" + address;
return zkClient.readData(addressPath);
} finally {
zkClient.close();
}
}
}
实现RPC代理rpcProxy
这里使用 Java 提供的动态代理技术实现 RPC 代理(当然也可以使用 CGLib 来实现),具体代码如下:
public class RpcProxy {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RpcProxy.class);
private String serviceAddress;
private ServiceDiscovery serviceDiscovery;
public RpcProxy(String serviceAddress) {
this.serviceAddress = serviceAddress;
}
public RpcProxy(ServiceDiscovery serviceDiscovery) {
this.serviceDiscovery = serviceDiscovery;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T create(final Class<?> interfaceClass) {
return create(interfaceClass, "");
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T create(final Class<?> interfaceClass, final String serviceVersion) {
// 创建动态代理对象
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
interfaceClass.getClassLoader(),
new Class<?>[]{interfaceClass},
new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// 创建 RPC 请求对象并设置请求属性
RpcRequest request = new RpcRequest();
request.setRequestId(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
request.setInterfaceName(method.getDeclaringClass().getName());
request.setServiceVersion(serviceVersion);
request.setMethodName(method.getName());
request.setParameterTypes(method.getParameterTypes());
request.setParameters(args);
// 获取 RPC 服务地址
if (serviceDiscovery != null) {
String serviceName = interfaceClass.getName();
if (StringUtil.isNotEmpty(serviceVersion)) {
serviceName += "-" + serviceVersion;
}
serviceAddress = serviceDiscovery.discover(serviceName);
LOGGER.debug("discover service: {} => {}", serviceName, serviceAddress);
}
if (StringUtil.isEmpty(serviceAddress)) {
throw new RuntimeException("server address is empty");
}
// 从 RPC 服务地址中解析主机名与端口号
String[] array = StringUtil.split(serviceAddress, ":");
String host = array[0];
int port = Integer.parseInt(array[1]);
// 创建 RPC 客户端对象并发送 RPC 请求
RpcClient client = new RpcClient(host, port);
long time = System.currentTimeMillis();
RpcResponse response = client.send(request);
LOGGER.debug("time: {}ms", System.currentTimeMillis() - time);
if (response == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("response is null");
}
// 返回 RPC 响应结果
if (response.hasException()) {
throw response.getException();
} else {
return response.getResult();
}
}
}
);
}
}
使用RpcClient类实现 RPC 客户端,只需扩展 Netty 提供的SimpleChannelInboundHandler抽象类即可,代码如下:
public class RpcClient extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<RpcResponse> {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RpcClient.class);
private final String host;
private final int port;
private RpcResponse response;
public RpcClient(String host, int port) {
this.host = host;
this.port = port;
}
@Override
public void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcResponse response) throws Exception {
this.response = response;
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
LOGGER.error("api caught exception", cause);
ctx.close();
}
public RpcResponse send(RpcRequest request) throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
// 创建并初始化 Netty 客户端 Bootstrap 对象
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(group);
bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel channel) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = channel.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(new RpcEncoder(RpcRequest.class)); // 编码 RPC 请求
pipeline.addLast(new RpcDecoder(RpcResponse.class)); // 解码 RPC 响应
pipeline.addLast(RpcClient.this); // 处理 RPC 响应
}
});
bootstrap.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true);
// 连接 RPC 服务器
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect(host, port).sync();
// 写入 RPC 请求数据并关闭连接
Channel channel = future.channel();
channel.writeAndFlush(request).sync();
channel.closeFuture().sync();
// 返回 RPC 响应对象
return response;
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
总结
本文通过 Spring + Netty + Protostuff + ZooKeeper 实现了一个轻量级 RPC 框架,使用 Spring 提供依赖注入与参数配置,使用 Netty 实现 NIO 方式的数据传输,使用 Protostuff 实现对象序列化,使用 ZooKeeper 实现服务注册与发现。使用该框架,可将服务部署到分布式环境中的任意节点上,客户端通过远程接口来调用服务端的具体实现,让服务端与客户端的开发完全分离,为实现大规模分布式应用提供了基础支持。